
by admin_lauth | Aug 28, 2018 | Investigations, Missing Person, News and Media, Tips & Facts
If you are a missing person, it helps to be white

(Jasmine Moody vanished in Detroit, Michigan on December 4, 2014.)
Jasmine Moody, a 22-year old Texas Women’s University student mysteriously vanished on December 4, 2014, while visiting a friend in Detroit, Michigan. Nearly four years later, police are no closer to figuring out what happened to her. News coverage of her disappearance has long since vanished from the scene too.
Approximately 7:30 p.m., the evening of December 4th, Jasmine was last seen leaving her friend’s home in the vicinity of the 3700 block of Baldwin, in the Van Dyke and Mack area of Detroit. Her family, who lives in Texas, is convinced foul play is involved in Jasmine’s disappearance and disappointed in the police department’s response and ensuing investigation.
“My daughter was real popular. She had a lot of friends. She was very social and energetic,” Jasmine’s mother Lisa Kidd told Dateline. “She always had a smile on her face. Always, always.”
Jasmine had known she wanted to be a nurse since she was 16 and described as a well-rounded student at Texas Woman’s University. According to her stepfather Patrick Kidd, Jasmine was a straight-A student, danced, and was training to be part of the U.S. Armed Forces through her school’s ROTC program.
According to police, Jasmine had developed an online relationship with Brittany Gurley, a woman who lived in Detroit. Just a few months after meeting online, Jasmine and Brittany had developed a strong friendship and Jasmine flew to visit Brittany and her family for Thanksgiving.
On the evening of December 4th, the two women allegedly got into an argument about Jasmine’s social media posts. Brittany and her family would later tell police that Jasmine put on a hoodie and walked out of the house.
Little else is known about her disappearance. No major ground search was conducted, and ongoing media exposure on a national level has been minimal.
 In contrast to Jasmine Moody’s case, Lauren Spierer, a 20-year old student at Indiana University, vanished June 3, 2011, after an evening out with friends in Bloomington, Indiana. Lauren, who grew up in Scarsdale, an affluent town in Westchester, New York. Her disappearance quickly garnered national press attention but remains unsolved.
In contrast to Jasmine Moody’s case, Lauren Spierer, a 20-year old student at Indiana University, vanished June 3, 2011, after an evening out with friends in Bloomington, Indiana. Lauren, who grew up in Scarsdale, an affluent town in Westchester, New York. Her disappearance quickly garnered national press attention but remains unsolved.
“Lauren’s disappearance has been and continues to be the most heart-wrenching experience of our lives,” Lauren’s family posted on Facebook on June 4, 2018, seven years after her disappearance. “I remember writing a few short months after Lauren’s disappearance that I never thought I would see an October without answers. I could never have imagined we would still be searching for Lauren seven years later. I end this now as I start each morning, hoping today will be the day.”
After an evening out at Kilroy’s Sports Bar with friends, Lauren was last seen on 11th Street and College Avenue in Bloomington at approximately 4:15 a.m. She had left her cell phone and shoes at the bar, presumedly taking her shoes off in the beach-themed bar’s sand-filled courtyard.
National news quickly began covering Lauren’s disappearance while hundreds of volunteers assembled to distribute thousands of fliers and help conduct ground searches of the area. A billboard overlooking the Indiana State Fairgrounds, along Fall Creek Parkway, asks the public for any information that would lead to the whereabouts of Lauren.

(Thousands of flyers of missing person Lauren Spierer have been distributed throughout the country.)
Hundreds of volunteers continued to turn out daily to help the family in their search.
Lauren’s case was profiled on popular America’s Most Wanted in 2011, leading to dozens of leads but not that one the family needed. Over the years, dozens of news media outlets have covered Lauren’s story.
Early on, Lauren’s parents hired private investigators and today, maintain an active Facebook group.
In one very revealing and heartfelt post, Lauren’s mother writes, “I could not have imagined on June 3, 2011, that my life would ever have any semblance of normalcy. Unfortunately, that word will never be applied to our lives. You learn to live with routines which get you through your days, weeks, months, and years. We will never know normal. Some of the things taken for granted in ordinary families are so far removed from ours it’s difficult to fathom. They range from everyday life events, a wedding, a birth and yes sadly death. What I wouldn’t do to hear Lauren’s voice or even just to notice a text on my phone. Something so simple as a text. My heart breaks at the thought of it. Well, those responsible will never be able to imagine. I have said it before and I know it’s redundant but what could have been an accident in a few short hours became a crime. The worst nightmare any parent or sister could imagine.”
Every day Lauren’s family simply hopes for answers. That’s all any family of a missing person could ask for.
Two young women, one black, one white, both ambitious students couldn’t be treated more differently by the media. One becomes nearly a household name, the other nearly forgotten. With absolute certainty, no one can say exactly why.
What are the numbers?
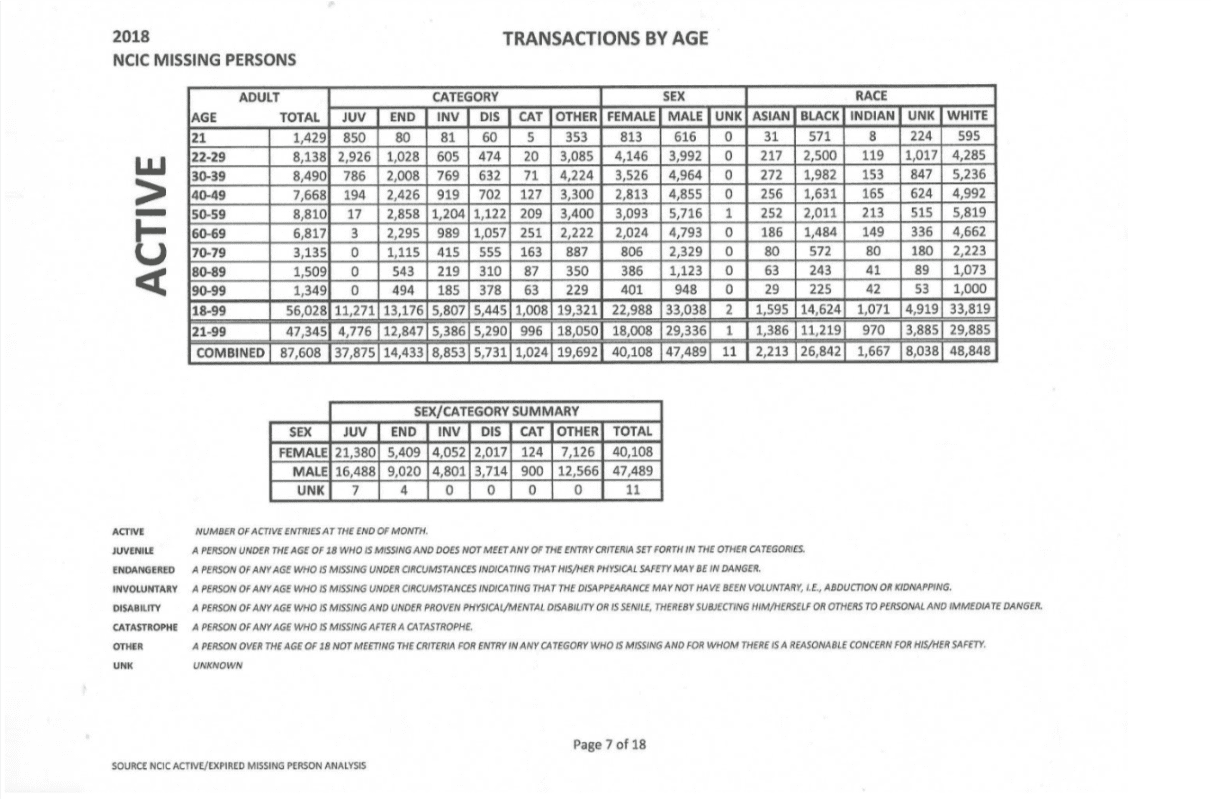
As of May 31, 2018, there were 87,608 active missing person cases in the National Crime Information Center (NCIC) database at the Federal Bureau of Investigation. Of the active missing person cases listed in NCIC, 40,108 cases are of missing women and 26,842 are black.

(National Crime Information Center Report)
Names like Chandra Levy, Laci Peterson, Elizabeth Smart, Polly Klaas, Natalee Holloway and Lauren Spierer have become familiar household names. Their missing person cases have dominated the headlines over the years. Cases like Jasmine Moody’s are not rare and unfortunately rarely make the local news.
Historically, whenever a female missing person becomes a national headline, she is almost certain to be a pretty, young white woman.
When was the last time you heard of a missing black female on CNN or other national news outlets?
In an NBC news story “Damsels in Distress” Roy Peter Clark, head of Poynter Institute for Media Studies is quoted, “It’s all about sex,” said Clark. “Young white women give editors and television producers what they want.”
“There are several common threads,” said Clark. “The victims that get the most coverage are female rather than male. They are white, in general, rather than young people of color. They are at least middle class, if not upper middle class.”
Some say the cases fit a narrative pattern that storytellers have used for more than a century, a pattern who design still incorporates remnants of an outmoded view of women and black people and their roles in society.
When it comes to popular stories, Clark said, “there is this perverted, racist view of the world. White is good; black is bad. Blonde is good; dark is bad. Young is good; old is bad. And I think we can find versions of this story going back to the tabloid wars of more than a hundred years ago.”
Regardless of class, color or age, it is clear that there is disproportionate coverage of black missing person cases. Referred to as “Missing White Woman Syndrome” and has led to a number of tough on crime measures named after white women who disappeared such as Suzanne’s Law, Kristen’s Law, Jennifer’s Law, Amber Alert and others.
In a study conducted by Baylor University, “The Invisible Damsel: Differences in How National Media Outlets Framed the Coverage of Missing Black and White Women in the Mid-2000s,” Professors Moody, Dorris and Blackwell concluded that in addition to race and class, factors such as supposed attractiveness, body size, and youthfulness function as unfair criteria in determining newsworthiness in the national news coverage of missing women. In addition, news coverage of missing black women was more likely to focus on the victim’s problems, such as abusive relationships, a troubled past, while coverage of white women tends to focus on roles as mothers or daughters.
Zach Somers, a sociologist at Northwestern University, noted that while there has been extensive research that shows that white people are more likely than people of color to appear in news coverage as victims of violent crime, there is relatively none when it comes to missing person cases.
Victim blaming appears to be compounding the unequal coverage and reinforces the view that black female victims are not only less innocent, but less worthy of rescue relative to white women. Thus, the term “Damsels in Distress.”
Others have blamed “police brutality” for the lack of publicity given to black female missing persons, attributing the silence to a habit of “sexism and patriarchy” in American society.

One group is fighting the imbalance of national media exposure that exists. The Black and Missing Foundation’s mission is to draw more attention to missing African Americans by providing an outlet for spreading the word through technology and print – and their work is making a difference.
By creating relationships with the media, government agencies, and the public, they are increasing the chances of missing black women being covered in the news and ultimately, to bring them home.
Derica and Natalie Wilson, two sisters-in-law, and founders of the Black and Missing Foundation have been profiled in People Magazine, Essence, Ebony, Huffington Post, Washington Post and developed a partnership with TV One. This year they celebrate ten years, helping thousands of families of missing persons and finding nearly 300 people.
“Many times, we are a family’s last resort – their last hope., says co-founder Natalie Wilson. This platform allows us to open our doors for families searching for their missing loved ones and not restrict access to help.”
Black and Missing Foundation have set the example for other groups to follow, especially the media.
Thomas Lauth of Lauth Missing Persons: an Expert in Missing Children and Adults noted, “In the 17 years of conducting missing persons cases for families and non-profit organizations, there is certainly a media and public bias against a missing person of color. When the general public and the media see a blonde 18 year-old on CNN that is missing–as opposed to an African American female on CNN–there is immediate attention to the blonde. Luckily there are non profit organizations such as Black and Missing to help bring more exposure to advocacy to the families for persons of color.”
Finding missing persons is a cooperative effort between the police, media, social service agencies and especially the public. With every news story, the coverage generates leads and increases the chance of that one lead being reported that will assist law enforcement in the investigation, and even close a case.
When it comes to missing persons there is no black and white, there are only families who are missing their daughters, siblings missing their sisters, children who are missing their mothers. There is no rich or poor, only families, human beings experiencing the most traumatic experience of their lifetimes.
People . . . who need our help.
For more of Kym Pasqualini’s work in missing persons, please visit her website, Missing Leads , or log on to Facebook and join the conversation on the Missing Leads Discusssion page!

by admin_lauth | Apr 23, 2018 | Consumer Fraud, Criminal Investigation, Missing Person, Personal Investigations
By: Kym Pasqualini, Lauth Investigations Feature Crime Writer

You receive a phone call and hear the voice of someone you don’t recognize. They tell you they have your child and will kill them unless you pay a ransom. They direct you not to call police or you will never see your child again.
What would you do?
You tell the person on the other end of the phone not to hang up. You don’t want to disconnect with the one person that can reunite you with your child. You plead for your child’s safe return. “Please don’t hurt her. I will do whatever you want,” you cry.
They demand you go to the bank and wire a ransom of several thousand dollars. Do you call the police? Do you pay the ransom and hope some thug will return your child to you safe?
A child going missing is every parent’s worst nightmare. For those who do have a missing child, living with such ambiguity is said to be the most traumatic of human experiences.
Sounds like a situation that only happens in the movies, right? Or, something only happening to the wealthy.
According to Newsweek, the Seattle Police Department is issuing warnings to parents advising scammers are targeting parents and demanding a ransom in exchange for the safe return of children they kidnapped . . . well, virtually kidnapped. Police throughout the country are following suit.

On March 8, 2017, in Ravensdale, Kings County, approximately 30 miles southeast of Seattle, a mother drops her children off at the school bus. Shortly thereafter, she receives a phone call from a man who threatened to kill her child if she didn’t pay a ransom.
The mother was able to reach out to the school to make sure her children were there. The school confirmed they were safe.
King’s County Sheriff’s Office told ABC News, this was the first reported incident in their jurisdiction.
In another case, a woman called a father “hysterically crying” claiming to be his daughter and stating she had been kidnapped. A man then got on the phone and told the dad if he didn’t pay a ransom, he would hurt his daughter.
Officers in Denver have responded to several reports of kidnappings. In a press release issued by the Denver Police Department, police say the caller demands a monetary payment in exchange for the release of the victim’s child. The caller dials the parents in the afternoon and demands the ransom to be wired to a bank.
After investigating the recent incidents in Denver, they determined the kidnappings were false and all children involved in the incidents were found safe.
Virtually Kidnapped Daughter
On Monday, April 16th, Sean Hollister was at his residence in Longmont, Colorado, about 15 miles northeast of Boulder, and received a frightening call from his 11-year old daughter who he thought was at school.
“My daughter was in tears, sobbing,” Hollister told the Times-Call. “I thought she was in trouble or something. She said, ‘Dad, I’m sorry I let this happen,’ which is exactly what she would say,” Hollister said.
“I said, ‘What’s wrong,’ and I offered up her name, so he knew my kid’s name,” Hollister said a man got on the phone and told him, “I got your daughter in a truck. She is on her way to Mexico.”
When Hollister told the man he was calling the police, the girl came back on the phone screaming. “Daddy, they are cutting me. Don’t call 911.”
Hollister was able to call police on his cell phone. “The caller told Hollister to get his wallet and identification and promptly leave the house.

Victims of “virtual kidnapping” describe the incident as traumatic.
Hollister’s postman was in the yard when he walked outside. “I’m mouthing ‘Help me,’ and he is freaking out,” said Hollister.
Longmont police showed up at his home fast and they took over from there and the caller hung up. Officers quickly determined Hollister’s daughter was safe.
The traumatized father would later find out the callers were trying to pull off a “virtual kidnapping” scam.
“The gap between the cops getting there and finding out my daughter is okay was terrifying,” said Hollister. “Who would think someone would be that cruel?”
Hollister’s caller had a Mexico number, but police say it is possible the caller was local and hijacked the number to appear like the call was made from out of the country.
In yet another case, a woman received a frantic call her brother had been kidnapped, injured and bleeding out, demanding thousands of dollars through a wire to return him safely. She was able to reach her brother on another phone and never paid any money, but a clear sign anyone can be a victim of this type of horrific scam.
According to FBI kidnapping expert, Agent Eric Arbuthnot, several organizations use these scams regularly to make money.
“Thousands of dollars in ransom,” said Arbuthnot. “And you’re talking about a criminal organization that is capable of doing more than one kidnapping at a time.”
According to Arbuthnot many of the cases have been happening on the West coast and along the border involving criminal organizations from Mexico, some claiming to be members of the cartel.
The FBI has seen recent increases in California, Nevada, New York, and Texas.
Monroe Police Department in Connecticut said by using social media, scammers can identify a victim, look up relatives, and reference names of family members and friends to make the call appear legitimate.
FBI Supervisory Agent Christopher Johnson said his office in St. Louis, Missouri deals with these types of crimes. “Scammers will often mention specific facts about the parent or victim, likely from information they were able to obtain online.”
Authorities say about one in five kidnapping cases are successful resulting in the criminal getting their ransom and not getting caught. While extortion has been around for decades, virtual ransom kidnapping calls are increasing around the country.

FBI Special Agent Glenn Milnor warns parents about virtual kidnapping.
With this emerging scam, the FBI has launched a nationwide campaign to warn parents to fight back against “virtual kidnapping.”
If you receive a virtual kidnapping ransom call…
Unlike traditional kidnapping schemes, a “virtual kidnapper” has not actually kidnapped anyone. According to the Federal Bureau of Investigation, if you receive a call from an individual demanding a ransom for the safe return of a kidnap victim, it is suggested you quickly evaluate the following to determine if you are receiving a legitimate ransom call:
- Caller insists you stay on the phone.
- Call does not come from your child’s cell phone.
- Caller tries to stop you from contacting the kidnap victim.
- Call includes demand for ransom to be paid via wire transfer.
- Ransom amounts may decrease quickly.
Knowing what to do
Police say it is best to hang up the phone; however, if you continue the conversation pay attention to the following:
- If you engage the caller, don’t call out your loved one’s name.
- Deliberately try to slow the situation down and ask to speak to your child directly.
- Ask “proof of life” questions like, “How do I know my loved one is okay?”
- To gain confirmation if your child is an actual kidnapping victim, ask questions only your child would know such as the name of a pet.
- Listen very closely to the voice of the person speaking. If possible record the call.
- Have someone else try to call your child’s cell phone, school, text, social media, etc., to confirm their safety.
- To buy time, repeat the caller’s request and tell them you are writing down the demand or tell the caller you need time to make arrangements.
- Don’t agree to pay a ransom: by wire or in person.
- Don’t deliver money in person.
- Immediately call your local FBI office and police.
According to the National Crime Information Center (NCIC), as of March 31, 2017, there were 86,618 active missing person cases in the FBI database, with 8,792 entered as involuntary.
Experts agree an actual kidnapping with a ransom demand is quite rare but all experts urge parents to be vigilant.
To read the FBI warning, please click here.

by admin_lauth | Apr 12, 2018 | Consumer Fraud, Phishing, Tips & Facts

In recent months, many Americans have been receiving calls from parts of the country they have never heard from before. They wonder to themselves, “Who could possibly be calling me from Bristol, Rhode Island? I don’t know anyone in Bristol.” They accept the call, and a voice will tell them that an agent with their firm has reviewed their case file, discovering that they hundreds of dollars in credit card debt, and must pay it all immediately, or else face a smattering of other fees for failure to pay. Fraught with the anxiety of their credit score tanking, they address an envelope to the P.O. box where the voice instructs them to send a check for the full amount. Before they place that envelope in the mail, hopefully they’ll realize they’ve just received a robocall.
They’re almost commonplace nowadays, regarded as more of a nuisance rather than a crime. Strange numbers automatically dial out to phone customers across the country, claiming they’ve won a free cruise or asking for donations to a fraudulent cause. However, many Americans are still not certain about what robocalls are, or the fact that most kinds are illegal.
Robocalls are just one of the latest tools in committing consumer fraud over the phone. There is a great deal of legislation  distinguishing which types of robocalls are legal. Conventionally they permit robocalls that convey important and/or emergency information, about things like school closures or natural disasters. With the rise of robocalls at the beginning of the millennium, the National Do Not Call Registry was established so that consumers could place themselves on a list in order to avoid them. However, legitimate telemarketing firms are still allowed to contact you over the phone for legal business, as long as your number is not listed on the Do Not Call registry, and you have not formally opted out of receiving phone communication from the business. Indiana law specifically requires that all prerecorded messages that bot calls are famous for must be introduced by a live operator, as well as providing an address where the caller can be reached.
distinguishing which types of robocalls are legal. Conventionally they permit robocalls that convey important and/or emergency information, about things like school closures or natural disasters. With the rise of robocalls at the beginning of the millennium, the National Do Not Call Registry was established so that consumers could place themselves on a list in order to avoid them. However, legitimate telemarketing firms are still allowed to contact you over the phone for legal business, as long as your number is not listed on the Do Not Call registry, and you have not formally opted out of receiving phone communication from the business. Indiana law specifically requires that all prerecorded messages that bot calls are famous for must be introduced by a live operator, as well as providing an address where the caller can be reached.
These types restrictions have forced the “robo-callers” to evolve and adapt. Conventional methods of blocking robocalls have been successful in nearly extinguishing the presence of calls to landlines. With smartphones only growing in use throughout the country, the technology designed to stop robocalls has not yet been perfected for them. The good news is that consumers (like the one receiving robo-debt-collection-calls) are never without resolve when it comes to harassing calls from a number claiming to be a collection agency.
Regardless of whom the robocall claims to represent, there is no legal obligation to speak to anyone over the phone. In the event that the call is legitimate, it is perfectly legal to communicate through your personal or business legal representation. If the call is legitimate, the lawyer can represent your interests and review your options with you. If you are without representation, you can also retain the services of a private investigator to ensure that the call is legitimate. The internet provides the ability to perform a reverse-lookup of suspicious or unfamiliar phone number, but most websites require that you pay for the search results, and after you pay, it might turn out that the information is inaccurate. The professional services of a private investigator allow them access to specific tools that provide accurate information to verify the legitimacy of the robocall. Bearing in mind that there is no agency sanctioned to harass you via telephone, consumers who sign up for the National Do Not Call Registry might find this is an imperfect solution. It will merely put you on a no-contact list required to be observed by all accredited, registered businesses. Although there might be a decrease in unsolicited calls, it still does not prevent illegitimate businesses to contact you with robocalls.
 The best recommendation that the Federal Trade Commission has made to consumers who are the victim of robocalls on their smartphones is downloading a third-party mobile app that uses both the hardware and the software of a smartphone to block robocalls from plaguing your mobile device,” “Call blocking apps let you create blacklists – lists of numbers to block from calling your cell phone. Many of these apps also create their own blacklist databases from numbers that have received significant consumer complaints. They also let you create whitelists – numbers to allow – that are broader than just your personal contacts.” This process has so far proven very effective. As users utilize the application, it builds a stronger wall that keeps unwanted robocalls out.
The best recommendation that the Federal Trade Commission has made to consumers who are the victim of robocalls on their smartphones is downloading a third-party mobile app that uses both the hardware and the software of a smartphone to block robocalls from plaguing your mobile device,” “Call blocking apps let you create blacklists – lists of numbers to block from calling your cell phone. Many of these apps also create their own blacklist databases from numbers that have received significant consumer complaints. They also let you create whitelists – numbers to allow – that are broader than just your personal contacts.” This process has so far proven very effective. As users utilize the application, it builds a stronger wall that keeps unwanted robocalls out.
The days of telemarketers who always call during dinner are long gone. Now robots are doing the dialing work. As technology advances, Americans feel more and more paranoid about ways the criminal element might have access to their money. Robocalls have only made it simpler to manipulate vulnerable consumers into parting with their hard-earned income. The Federal Trade Commission is attempting to evolve even faster than scammers, developing technology similar to apps like RoboKiller and Nomorbo that can keep robocall schemes at arm’s length. Professionals like lawyers and private investigators are invaluable sources when validating the legitimacy of a robocall a consumer fears might be legitimate. The most important resource, however, is an informed consumer. Vigilance and skepticism are the first line of defense when dealing with robocall consumer fraud.

by admin_lauth | Mar 21, 2018 | Corporate Investigations, Private Investigations News
Written By: Kym Pasqualini, Feature Crime Writer for Lauth Investigations
When we think of a spy, given the national news cycle, it may conjure up thoughts of Russians or the Chinese who have been long known for hacking and espionage. However, even more common, but much less talked about, is the business mole, and almost every business in America is susceptible.

Every business sector is vulnerable to Corporate Espionage costing businesses billions of dollars per year.
April 10, 2011, Joseph Muto was hired to work for the top-rated “O’Reilly Factor” but within 3 days, he was discovered by Fox employees to be anonymously writing for Gawker. In the span of 72 hours, Muto wrote a series of articles detailing the internal workings of the network, along with stealing and selling raw video clips. In 2013, he pled guilty to two misdemeanor charges and was dubbed the “Fox Mole.” He was fined $1000 and sentenced to over 200 hours community service. At sentencing, he said he wished he had never betrayed his former employer.
United States industries spend more on research and development of unique products and processes than any other country in the world. The key to success is having an “edge” in the business world. Whether a media company, software developing company or bakery, keeping an edge is key.
When someone steals those “trade secrets”, it is called economic espionage and costs American businesses billions annually. Damages can severely destabilize the victim company to include lost revenue, lost employment, lost investments, interruption in production, damaged reputation, and can even result in a company going out of business.
Corporate espionage conducted by spies or moles believe computers are irrelevant. It is about what data they want, what form they take, and how they can steal it.
The Company Man
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) states no business, large or small, is immune to the threat of moles and/or spies. Any proprietary process, product, or idea can be a target.
To raise awareness, the FBI in collaboration with the National Counterintelligence and Security Center has launched a nationwide campaign and released a short film called “The Company Man: Protecting America’s Secrets,” based on a true story. Mr. Moore is both unappreciated and unhappy with his career as an engineer at a glass insulation and fire-retardant firm. He is targeted on LinkedIn by a competitor who offers him a position in a rival firm. At first, Moore declines because he signed a non-compete. He is then offered $200,000 to obtain plans for equipment and formula for the glass insulation produced at his firm, RIS.

The FBI states many things drive a person to betray the company where they work.
Moore makes the decision to go to his current boss who then contacts the FBI who initiates a sting. A true story, there was an arrest in the case. However, this may not be the decision every employee would make – which makes every employee a liability in a 400 billion, in the dark. underbelly of America’s global economy.
Spotting Insider Threats
What drives a mole? The FBI states company moles are often “overwhelmed by life-crisis or career disappointment” driving them to leak information.
With email, cell phones, and jump drives, stealing information is far easier than in the past. Greed and financial need, unhappiness at work, the promise of a better job, drug or alcohol abuse, and/or vulnerability to blackmail, can all be contributors, says the FBI.

The FBI says employees who leak trade secrets, such as plans, customer databases, etc. will exhibit behaviors other employees can often identify to help prevent breaches.
Your employees may be the first line of protection when combatting the insider threat.
Potential Indicators:
- Drastic changes in behavior, demeanor, or work habits.
- Unexplained affluence.
- Financial hardship.
- Substance abuse.
- Attempts to circumvent security procedures.
- Long hours at the office without authorization.
- Taking home proprietary information.
- Unnecessarily copying materials.
- Using an unauthorized USB drive.
- Unusual use of cell phone during business hours.
- Asking inappropriate questions.
- Suspicious relationships with competitors.
- Leaving traps to detect searches of their office.
Based on FBI’s studies, additionally, there are more subtle things to look for:
- Someone hired to steal company information will be experienced in the operation of a business and will be able to identify the value of your company’s trade secrets.
- Corporate spies are everyone’s friend. To gain access to a company in order to steal information, a mole will be socially adept with the ability to manipulate people to gain their trust.
- Individuals who are frequently wandering or talking in locations they do not need to be to complete their job. Someone who reflects a pattern will always have a reasonable excuse as to why they are not in the correct area or talking to specific employees.
- Employees who keep trying to re-open decisions already settled and question advisability of decisions.
- They act envious.
Vulnerabilities – Getting Access
Once inside, a mole has a lot of ways to access sensitive information. Spies can even work in pairs, possibly one as a consultant and the other an employee. When you have valuable information, never underestimate the methods others will use to gain access to it.
Spying can be as easy as photocopying papers found on unattended desks or at printers. Walking into an empty meeting room with a laptop and pulling data off the network.
A common ploy is pretending to be an employee. Another ploy often used, posing as IT personnel because it enables the individual to look legitimate while accessing network access points and sitting at someone’s computer. In other cases, spies have posed as cleaning staff, gaining access after-hours.
Criminals capitalize on the common assumption if you are in the building, you must be okay. Investing in your company’s staff to raise awareness is the best investment a company can make.
According to InfoWorld, Peter Wood, Chief of Operations at First Base Technologies, a U.K. based consultant firm performing ethical hacking services, “Spies are interested in anything from financial data to intellectual property and customer data. They might steal information for blackmail purposes, but the most common motive for physical intrusion is industrial espionage.”
Wood says the most common way to intrude upon a company is posing as an employee or a visitor, even creating convincing costumes to pose as a legitimate visitor such as telephone, electrical or maintenance person, a burglar alarm inspector, even someone from the fire department.
Protecting Your Trade Secrets
The FBI lists several ways to protect your workplace from insider threats.
- Recognize the threat.
- Identify and value trade secrets.
- Implement a definable plan for safeguarding trade secrets.
- Secure physical trade secrets and limit access to trade secrets.
- Provide ongoing security training to employees.
- Use protective tools such as screensavers with password controls.
- Classify information and store accordingly.
- Secure the workplace so visitors do not have access without security screening.
- Encrypt data and require strong passwords for employees with liberal access rights.
- Develop an insider threat program.
- Proactively report suspicious incidents to the FBI before your proprietary information is irreversibly compromised.
- Ask the FBI or other security professionals for additional awareness training.
At times, companies are hesitant to report such activity for fear they will risk their trade secrets being disclosed in court or compromised in any way. The FBI will do all it can to minimize business disruption, safeguard data and privacy, and will seek protective orders to preserve business confidentiality and sensitive information. The Department of Justice also has a variety of protections in place to ensure information is protected during a criminal prosecution.

by admin_lauth | Feb 23, 2018 | Private Investigations News
By: Kym Pasqualini, Feature Crime Writer for Lauth Investigations
On February 13, 2017, best friends Abigail “Abby” Williams, 13, and Liberty “Libby” German, 14, planned to go hiking near the beautiful area of Monon High Bridge Trail, east of their small town of Delphi, Indiana.

Libby German and Abby Williams, Best Friends
At approximately 1:45 p.m. that afternoon, a family member dropped them off at the abandoned bridge where they planned to hike. It was agreed they would meet their family back in the same location later in the afternoon. They both had the day off school, it was an unseasonably warm winter day, and Abby Abby and Libby shared a special friendship. They both loved hiking, taking photographs of flowers and trees, and adventuring the scenic trails about a mile east of their home.
Libby posted, this now haunting photo, while atop Indiana’s second highest bridge on her Snapchat at 2: 07 p.m. This was the last post anyone would see the two girls alive.

Photograph Libby posted on Snapchat of Abby walking on the Monon High Bridge, Dephi, IN.
When the girls did not show up at the agreed upon the location as planned, the family reported the girls missing to Delphi Police Department and the local sheriff. Immediately police and firefighters were dispatched to canvas the area.
Over 100 searchers responded to the area. Arial searches began utilizing the remaining daylight hours. Later the same evening, authorities began trying to “ping” the girl’s phones, with no success. The sheriff stated he felt the girl’s phones were either turned off or the batteries had gone dead.

Police searching for Abby and Libby in the area surrounding Monon High Bridge and Deer Creek trails.
At approximately midnight, the search was called off, though volunteers continued searching throughout the night. The search resumed the following morning along Deer Creek and farther out from the trail. Searchers prayed the girls had simply been lost but soon those hopes were dashed. Approximately one mile from where the two young girls vanished, searchers found two bodies on a piece of private property along Deer Creek, north of the bridge.
February 14, 2017, at approximately 1:50 p.m., Sheriff Leazenby, Delphi Police Chief Steve Mullins and Indiana State Police (ISP) representative Kim Riley held a joint press conference to announce two bodies were found during the search for Abby and Libby, stating the bodies had yet to be identified.
February 15, 2017, 2:33 p.m., authorities held another press conference and announced the bodies had been identified as Liberty German and Abigail Williams.
A community was heartbroken. Children were terrified, and parents held their children closer.
Haunting Images and Audio Found on Libby’s Phone
At the February 15th news conference, ISP proceeded to release a photo of an unidentified man walking along the Delphi Historic Trail found on the girl’s phone. Authorities announced they wanted to speak to anyone who had parked in the nearby lot or anywhere around the trail the day the girls had visited the park.

FBI names individual in photograph suspect in murder of Delphi girls.
Five months into the investigation, ISP released a composite sketch of the man on the bridge hoping someone may recognize him and make a call.
Chilling audio of the killer’s voice Libby captured on her phone was also released generating thousands of leads.

In an Indy Channel report, “Delphi Investigation: Why state police say Libby and Abby’s case isn’t cold,” Indiana State Police Superintendent Doug Carter says, “There’s a person out there that knows who did it. Not a hunch. They know who that person is,” said Carter. “They know that voice and they know those clothes. They know that posture. They know that stance and they know who murdered those two little girls in that quiet place.”
March 1, 2017, former Indianapolis Colts punter Pat McAfee and team owner Jim Irsay donate $97,000 to the reward fund. The reward is now $230,000 for information leading to the arrest and prosecution of the individual who murdered Abby and Libby.
In an ABC RTV6 report, “Delphi, Indiana: FBI seeks tips on behavioral changes to help catch Delphi killer,” the FBI makes a plea to the public to think back to Monday, February 13th, the day the Delphi teens went missing asking questions like, “Did someone you know make an excuse for missing an appointment?”
“Just think if you had an interaction with an individual who inexplicably canceled an appointment that you had together,” said Greg Massa of the FBI. “Or an individual called into work sick and canceled a social engagement. At the time, they gave what you thought would have been a plausible explanation. ‘My cell phone broke’ or ‘I had a flat tire on my car.’ In retrospect, (that) excuse no longer holds water,” Massa added.
Other behaviors might now be considered suspicious. It is often a seemingly inconsequential detail someone calls in that can break a case wide open.
“Did an individual travel unexpectedly?” Massa said. “Did they change their appearance? Did they shave their beard, cut their hair or change the color of their hair? Did they change the way they dress?”
Even behavioral changes occurring shortly after February 13, 2017:
- Someone who developed a different sleep pattern
- Started abusing drugs or alcohol
- Has become anxious or irritable
- Someone who has followed this case to an extreme
- A person who has ongoing conversations about where they were February 13th
- Someone who has visited the location where the girls were murdered
- Someone who has taken photographs around the trail and bridge
Police say don’t ever feel bad about reporting odd behavior. It could have everything to do with finding justice for two little girls brutally murdered. It could save other children from a similar and tragic outcome. In addition, if the person is innocent, it will only take a couple minutes of their time and they will never know you were the one who made the report.
A Person of Interest Dismissed
Johnson County Sheriff’s Office sent officers to Colorado to retrieve a “person of interest” in the murders of Abby and Libby.

Daniel Nations had been arrested in Colorado for threatening hikers with a hatchet on a Colorado trail. Investigators traveled to Colorado to question Nations.
Nations was wanted on an outstanding warrant in Johnson County, Indiana for failing to register as a sex offender so authorities brought him back for further questioning in the Delphi murders.
Police have not formally named Nations as a suspect stating they have no information specifically including or excluding Nations in the killings. However, ISP has since said they are no longer actively investigating Nations as a person of interest in the case.
Memories Keep the Families Going
In “Delphi Daughters: The Untold Story of Abby and Libby”, a News 6 report, Mike Patty Libby’s grandfather states, “They didn’t leave each other’s side,” about the afternoon the two girls vanished. “I don’t know what happened out there that day, whether there was a chance or an opportunity for one to break off or split, or make a break for it or whatever but you know, I look at it as two young soldiers who covered each other’s backs, two best friends, I wouldn’t leave my best friend’s side. Neither did they.”
They both loved music. Both played the Alto Saxophone in their middle school band. They loved photography and painting, and both were signed up to play softball.
Life has changed for both families. Libby is remembered as the “baker” of the family. She loved making chocolate chips cookies. Becky Patty, Libby’s grandmother said, “She was a baker. She could throw a batch of cookies together like no other.”
Libby loved using sticky notes. She would leave sticky notes on her grandmother’s car visor. One read, “I love you! Thank you for everything you do for me and Kelsie – Libby.” She would leave sticky notes all over the house, even giving her teachers sticky notes, and always showing her appreciation for everyone around her.

Libby German and best friend Abby Williams, loved and remembered by all who knew them.
In the aftermath of her murder, Libby’s class presented her grandparents with jars filled with “sticky note” messages from each child. A way of dealing with the loss for her classmates, and a reminder of how much she is missed.
Libby had dreamed of becoming a science teacher and loved finding cures and solving crimes, so much so, she took additional classes at Purdue University.
Like Libby, Arika Gibson, a friend of the pair said, “Abby also dreamed of doing something within forensics and police work.” For two amateur sleuths, clearly, the evidence the girls left on their cell phones was clues to their own murders.
Abby Williams’ grandparents, whom she called Mee-maw and Papaw, keep her belongings right where they were the day she disappeared. “We just can’t erase her from our lives, we just don’t want to.” She added, “We treasure her coat hanging on the coat hook, her shoes on the shoe rack and her bedroom just the way she left it – she may have walked out the door, but she is here with us,” said Diane Erskin, Abby’s grandmother. With tears in Abby’s mother’s eyes, Anna Williams added, “Abby smiled all the time.” Her voice to a whisper, “All the time.”
Abby’s favorite thing to say was, “Is there anything I can do to help?” Always with a joyful spirit. Anna and her daughter Abby both shared a love of photography. She loved arts and crafts even knitting hat for newborns with her Aunt Maggie. She was especially good at volleyball and had planned on starting softball with Libby in the new year. Her grandfather Cliff was so excited he drove down from Michigan to take Abby out shopping to buy all new gear.
Investigation Continues at God Speed
The search for a killer has reached national proportions. Approximately 6,000 electronic billboards in 46 states have been utilized to solicit information from the public.

Billboards with information about the Delphi murders have been placed throughout the country.
A year later, investigators have received over 30,000 tips and interviewed thousands of potential suspects.
ISP, FBI, Carroll County Sheriff and the Delphi Police Department still follow up leads and vow to solve this murder case.
Investigators have a motto, “Today is the day,” and each day at the department, the day starts out with a prayer. “As we gather together today for our work we have been assigned to, let’s pray,” as each investigator bows their head.
“Today’s the day, today is the day we are going to get closer to the end, today is the day we are going to get closer to getting justice for Abby and Libby,” said ISP First Sergeant Jerry Holeman. “We have all worked tragic cases. Nothing like this. I can’t put anything close to this case.”
Police continue to work 20 hours days, with sleepless nights, with one goal in mind. A team of hundreds of investigators continue to work the case, tracking down thousands of leads. Holeman admits it has been rough on everyone involved. Investigations can become a roller coaster ride with hopeful leads and dashed hopes when those leads are eliminated. When it gets tough, Holeman goes back to the saying, “Today is the day.”

Indiana State Police Sgt. Holeman interviewed by Alexis McAdams. Photo courtesy Alexis McAdams TV.
“I need to be here for Abby and Libby,” says Holeman, “Because I am going to find who did this and we are going to hold them responsible for their actions.”
When Anna Williams was asked what justice will look like for her, “Justice will be that deep breath we get to take when my friend’s children are sleeping in their beds again. When people don’t worry about their children playing outside.” Williams continued, “Justice is in law enforcement. We believe in law enforcement. We believe in the FBI and everyone else that has worked on this case. That’s where justice will come from.”
Unsolved homicide posters still hang in local company’s windows. The community stands united behind Libby and Abby’s families and law enforcement still working the case.

Source: Facebook Light Up for Abby and Libby.
Orange bulbs light up the entire town of Delphi. The community has committed to ensuring the golden glow lights the town until the killer of Abby and Libby is caught and brought to justice.
If you have any information about the murders of Abby Williams and Libby German, please call 844-459-5786 or ABBYANDLIBBYTIP@CACOSHRF.COM.


 In contrast to Jasmine Moody’s case, Lauren Spierer, a 20-year old student at Indiana University, vanished June 3, 2011, after an evening out with friends in Bloomington, Indiana. Lauren, who grew up in Scarsdale, an affluent town in Westchester, New York. Her disappearance quickly garnered national press attention but remains unsolved.
In contrast to Jasmine Moody’s case, Lauren Spierer, a 20-year old student at Indiana University, vanished June 3, 2011, after an evening out with friends in Bloomington, Indiana. Lauren, who grew up in Scarsdale, an affluent town in Westchester, New York. Her disappearance quickly garnered national press attention but remains unsolved.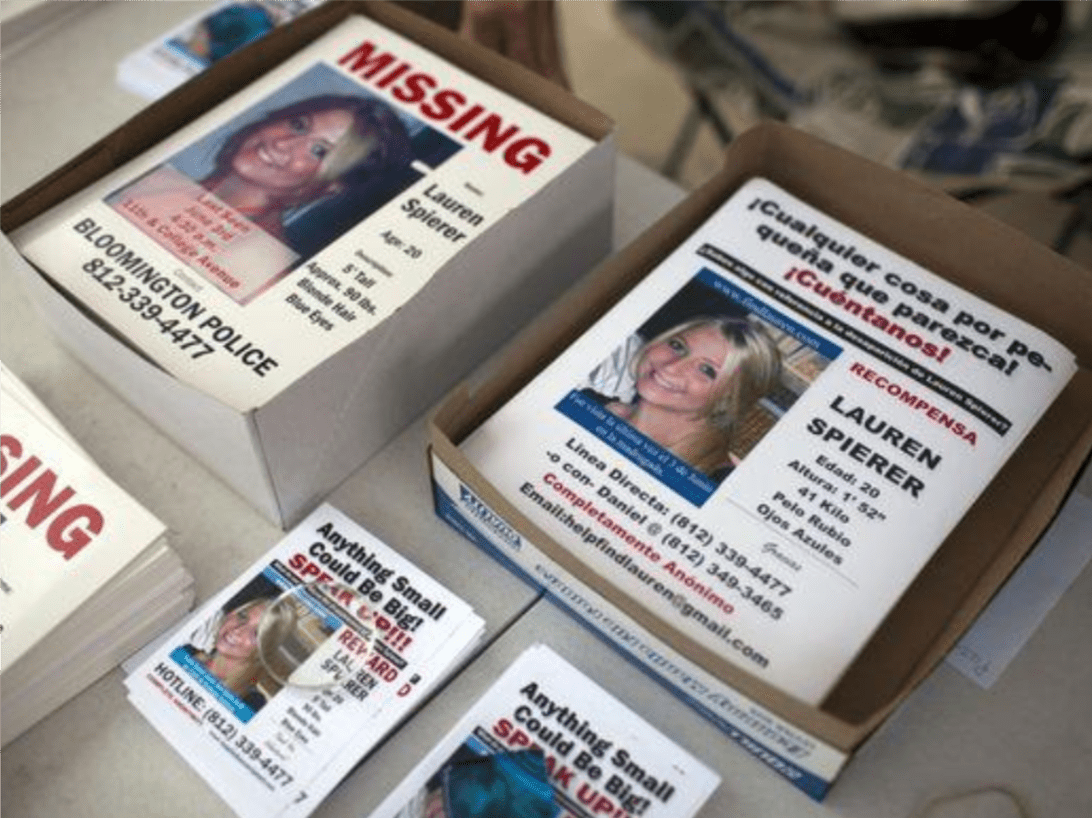







 distinguishing which types of robocalls are legal. Conventionally they permit robocalls that convey important and/or emergency information, about things like school closures or natural disasters. With the rise of robocalls at the beginning of the millennium, the
distinguishing which types of robocalls are legal. Conventionally they permit robocalls that convey important and/or emergency information, about things like school closures or natural disasters. With the rise of robocalls at the beginning of the millennium, the  The best recommendation that the
The best recommendation that the 











